What Is The Difference Between Vinyltirethoxy Silane And Vinyltrimethoxy Silane
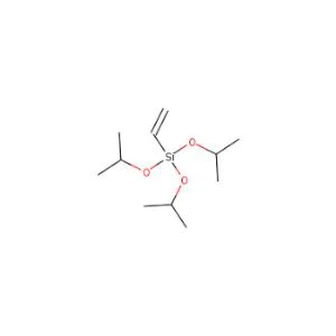
Vinyltriethoxysilane (VTES) and Vinyltrimethoxysilane (VTMS) are two silane coupling agents used in the production of a range of industrial materials. Although they have similar chemical structures, there are some fundamental differences between these two silanes that make them suitable for different industrial applications.
One of the primary differences between VTES and VTMS is the length of their alkyl groups. VTES has a longer alkyl group than VTMS, which makes it more soluble in water. As a result, VTES is often used as a coupling agent in the production of water-based coatings, adhesives, and sealants. In contrast, VTMS is more suited to oil-based systems and is commonly used in the production of rubber and plastic materials.
Another significant difference between the two silanes is the rate of hydrolysis. VTMS undergoes hydrolysis faster than VTES, which makes it more reactive and ideal for use in cross-linking applications. In addition, the rapid hydrolysis rate of VTMS also makes it more suitable for use in low-temperature curing systems. VTES, on the other hand, has a slower hydrolysis rate, which makes it more suited for high-temperature applications.
One advantage of VTES is its high degree of adhesion and strong bonding properties. This makes it particularly useful in the production of composites and laminates, where a strong bond between different materials is essential for their performance. VTES is also used as an adhesion promoter in the production of paint and coating systems, where it improves the adhesion and durability of the finished product.
In contrast, VTMS is highly effective in the reinforcement of rubber and plastic materials. Its ability to improve the physical properties of these materials, such as tear strength, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, makes it an essential component in the production of tires, gaskets, and seals, among others.
In conclusion, VTES and VTMS are two fundamentally different silanes with unique properties that make them suitable for different industrial applications. VTES is ideal for water-based coatings, adhesives, and sealants, while VTMS is suited for oil-based systems and rubber and plastic materials. Understanding the differences between these two silanes is crucial when selecting the appropriate coupling agent for a particular application, as it can significantly impact the performance, durability, and efficiency of the finished product.